
Login Form
Need help finding the perfect solution or services to fit your company's needs?
We have the answers!
IPITEK is Driving IPTV in the New Media Era
With video as the major source of traffic on the internet we are living in the midst of the internet video revolution. This pattern is increasing exponentially! The two primary drivers of the video revolution are: (1) increasing penetration of broadband access technologies and (2) the development of easy-to-use video content creation. The IPTV video revolution has changed all of our concepts about the basics of video transport. Video creation and distribution are now accessible to anyone. The video market is undergoing rapid changes in technology driven by consumer demand for all forms of video (TV, video on demand, Internet, and peer to peer file sharing networks).
Future video services will be delivered over packet based (dominantly IP/Ethernet) networks. However, the requirements for video services are distinctly different from the requirements for data Internet services. This poses major challenges to the architecture, design, and provisioning of video services.
For over 20 years - from the development of its earliest video transport products to their newest products, IPITEK has provided the video transport industry with many solutions that meet and exceed industry requirements. This paper outlines the requirements of future video services such as IPTV, Video on Demand (VOD), Internet Video, etc. It also illustrates the challenges operators face when such services are considered as well as shows how IPITEK's decades of experience and expertise in delivering video-optimized solutions and its DNA for integration has enabled IPITEK's technology to provide revolutionary end-to-end solutions for future video applications.
IPITEK and the Video Revolution: User Needs and Provider Challenges
There is a natural conflict emerging between consuming video over the Internet or from the TV. Data and video communication are converging. In fact, most of the new digital TVs have Ethernet ports. Thus, it is impossible to separate the Video revolution from the data and the internet revolution. In this context, it is extremely important to distinguish between two (usually confused) terms: IPTV and Internet Video.
- IPTV: IP protocol is used to transport, manage, and distribute video from video sources (head-ends) to end-users or customers at homes.
- Internet Video: these are the video material such as video clips that are located on Internet servers such as YouTube and Netflix.
Despite this distinction, both IPTV and Internet Video are driving this revolution. IPITEK, with its long-standing history, is on top of this revolution by providing solutions for both IPTV and Internet Video.
With telecommunications shifting towards IP-based solutions, operators are consolidating their infrastructure towards packet-centric networks. IP/Ethernet transport is becoming a more widespread way of carrying media services as older but more reliable, SONET/SDH-types of connections, become difficult to obtain or are priced at a high level. The operational benefits of transporting traffic (video, voice, and data) over converged IP/Ethernet networks are substantial. However, for media services it is critical to select an IP transport solution that delivers the required quality of service and manageability with a minimum of complexity.
The architecture of an IPTV network is shown in Figure 1.
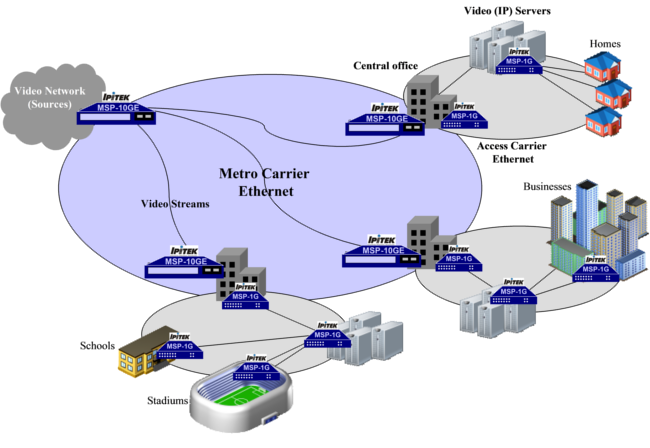
Figure 1: IPITEK IPTV Solution
In IP/Ethernet networks, packets are transported using resources (links, switches, and routers with packet buffers) that are statistically shared with traffic from other sources through the network, giving a flexible utilization of the network resources. However, as the resources are shared, it is quite difficult to guarantee the transport. Nevertheless, service providers that compete for market share in next-generation consumer entertainment and communications services must move beyond "bundling" and offer personalized media and interactive IPTV services that blend entertainment, communications, and Internet. With the deployment of these new IPTV services, existing network infrastructures must be scalable to support millions of customers, maximize bandwidth resources, and provide quality of service (QoS) with security on an end-to-end basis. For these and other reasons, network intelligence is critical when deploying video over broadband and that makes IPITEK's MSP-10GE, MSP-1GE, and MSP-CES ideal transport solutions.
As IPTV services explode in mainstream deployment, video quality metrics are paramount to attract and retain customers at all levels; spanning Contribution to Distribution networks. As the newest replacement technology, it is clear that IPTV services must exceed video quality benchmarks established by their legacy network. All components in the video delivery chain must measure up to the QoS and Quality of Experience (QoE) requirements that the end-customer/subscriber is accustomed to and expects.
The most common business challenges for IPTV are to add and properly manage these high demand, high margin, high QoS/QoE video service capabilities in a cost effective manner with all current existing services, upholding previously defined quality parameters. Additionally, customer demands for instant or nearly instant service provisioning and de-provisioning are today's norm. In order to accomplish this cost-effectively and thoroughly, a flexible, comprehensive, on-the-fly means to properly provision, manage, monitor and control varying video service types across the network needs to be in place. Today's market is growing more and more intolerant of waiting days or even hours to provision and implement new services.
Overall, such performance requirements are imposing substantial challenges and demands on a network forcing it to be very dynamic, intelligent, bandwidth-optimized, managed, and QoS-capable. This will allow for maximum efficiencies and revenues under dynamic network conditions. These must also be augmented by real time video management and provisioning of video in IP environments.
IPITEK's Ethernet-based IPTV Solutions: The Need for Carrier-Class Functions
IPITEK's Carrier Ethernet video-optimized solutions support functions that allow for Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) capacities for IPTV networks. Specifically, the following standards have been developed for OAM support in Ethernet networks:
- IEEE 802.3ah Ethernet Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM): (802.3ah Ethernet OAM is known as "link OAM" since it runs over a point-to-point 802.3 link). E-OAM provides mechanisms such as link monitoring, remote failure indication, remote loopback control, and OAM discovery. E-OAM uses a simple OAM PDU frame that runs directly over a standard Ethernet MAC header. OAM provides useful fault management capability, including fault isolation, fault detection, and link performance testing. E-OAM is considered most useful in "the last mile" to monitor Ethernet access services, but can also be used on any Ethernet link in the network.
- IEEE 802.1ag Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (E-CFM ): 802.1ag Ethernet CFM runs end-to-end over an Ethernet virtual circuit and is viewed as a critical component for delivering carrier-grade Ethernet services. E-CFM includes protocols that provide the ability to detect, verify, and isolate connectivity faults. It also runs directly over standard Ethernet frames that travel in-band with customer traffic. Devices that do not support E-CFM will forward the frames and not participate in the messaging. The three E-CFM protocols are continuity check, loopback, and linktrace. Continuity check provides a keep-alive type of message over an Ethernet service and is used to detect and notify that a fault has occurred. The loopback protocol is like an IP ping at Layer 2. A loopback message (LBM) and a loopback reply (LBR) verify any faults. The linktrace protocol is like an IP traceroute at Layer 2. There is a linktrace message (LTM) and a linktrace reply (LTR) that isolate faults. E-CFM can define hierarchy within a domain, which gives an administrator visibility into specific nodes along the path.
- ITU-T Y.1731: The Y.1731 specification is a superset of 802.1ag. It provides all the features of E-CFM, plus the following signals: Ethernet locked, Ethernet test, multicast loopback, and alarm indication. Performance management capabilities include frame loss measurement, frame loss delay, and throughput measurement. At this point, Y.1731 is not widely implemented, but with its enhanced capabilities, it is of great interest to service providers.
- Advanced network timing: Timing and synchronization is an extremely important application in IPTV. Note that with synchronization in IPTV, Telcos can effectively compete against cable TV operators. In fact, video is very susceptible to latency and loss of frames. Network latency jitter affects the QoE of the viewer because artifacts, pixellation, blurring, or audio distortion are very noticeable events. Given these challenging synchronization requirements, IPITEK supports the synchronization solutions:
- Network synchronous methods (that is, reference timing signal distributed over the synchronous physical layer). IPITEK' MSP-CES achieves that by supporting Synchronous Ethernet (Sync-E) on any of its Ethernet ports. Enabling Sync-E on any port is user selectable.
- Packet-based methods: Packet-Timing Protocols (PTP) such as IEEE1588v2 belong to this category. IPITEK achieves this by using its ultra-small standalone IEEE1588v2-based platform, the MSP-1588, to provide synchronization. The MSP-1588 supports all telecom-profile modes of operation including master, slave, and transparent (timing repeater). By relying on a standalone solution, network operators can build extremely accurate timing "overlays" on top of their networks. The beauty of the standalone solution is that it allows for building user-customizable and upgradable network timing overlays that perfectly fit end user applications from mobile backhaul to TDM business services to PBX interconnection, wherever needed, whenever needed.
- IPITEK's MSP-CES, one of its Carrier-Class Ethernet offerings, relies on internal oscillators such as a TCXO or OCXO to provide a Stratum 3 or 3E quality clock. The systems timing module can also be driven by an external input coming on the BITS interfaces.
In a nutshell, Ethernet has evolved as a carrier-grade transport technology in which IPITEK is a major player. This allows for rapid deployment of Ethernet in networks to support IPTV services while substantially cutting costs and exceeding QoS and QoE standards required by the IPTV application.
IPITEK's IPTV Solutions: From Contribution to Transport to Distribution
Another critical part of IPTV networks is to provide solutions for video sources. Today's video networks can involve many parties and applications. These functions can include:
- Interconnection between local or regional TV stations and the broadband cable headend
- Transport to and from off-site facilities and venues
- Interconnection from the TV station main studios to the transmitter
- Recovery of engineering signals from remote receiving locations with transport to a studio or editing suite
Responding to these expanding industry requirements, IPITEK has developed a wide range of Digital Transport Platforms that offer ideal solutions for digital network interconnect carrying a wide variety of traffic. IPITEK's HBR-2502 Digital Transport Platform offers features designed to provide the most efficient transport of network signals and uses the most advanced method of bandwidth assignment in the industry, which means HBR users can move more traffic more efficiently in the same 2.5 Gb/s bandwidth as compared to other systems.
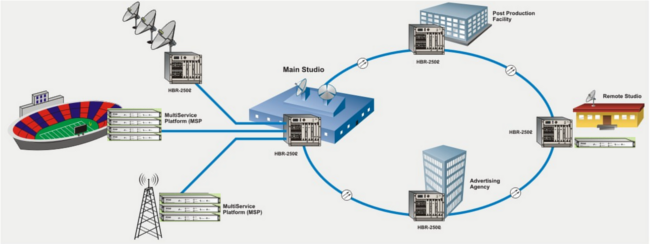
Figure2: IPITEK Video Contribution Solutions
In order to meet the rapid transition to digital TV, Cable and television operators require an efficient and economical solution to transport Baseband analog and HDTV digital signals from broadcasters studios or other video origination points to the cable headend. The MSP-110 Transport System provides an efficient interconnect between television stations and cable headends. This new platform offers a solution that combines both standard analog Baseband and DVB-ASI HDTV signals onto a single fiber.
In addition, IPITEK's MSP-220 Transport System offers many additional capabilities and solutions. MSP-220 combines very high performance 12 bit analog signals with full 270 Mb/s HDTV (SMPTE 259M) and 100 Mb/s Ethernet onto a single fiber. The MSP-220 extends performance even more by offering an option for Gigabit Ethernet (GigE) transmission as well. This new combination is not only cost effective but provides additional solutions for transport of the highest performance video signals over a single fiber.
IPITEK is currently developing a highly-integrated 3G HD transport solution that supports bi-directional transport of auto-detectable digital video signal formats including 2.967Gb/s 3G-SDI (SMPTE 424M), 1.485Gb/s HD-SDI (SMPTE 292M), and 270Mb/s SD-SDI (SMPTE 259M-C, ITU 656).
Figure 3 shows an example of IPITEK's HBR-2502/MSP-110 (MSP-220) being used in a video contribution architecture.
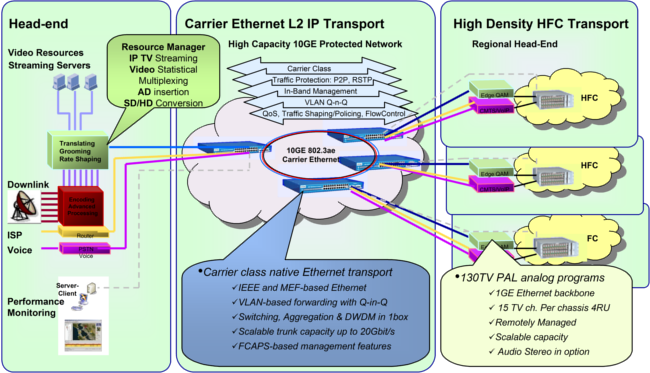
Figure3: IPITEK Solution for Contribution, Transport, and Distribution
IPITEK's revolutionary technologies that are optimized for video transport can provide an end-to-end solution for IPTV networks starting from video contribution (head-end) to video transport (using carrier-class video-optimized Ethernet) to video distribution. An example of the advanced hybrid fiber-coaxial solution (HFC) is depicted in Figure 3.
Summary
IPITEK's decades of expertise in developing video-optimized solutions and its DNA for integration have enabled its technology to provide revolutionary end-to-end solutions for future video applications. IPITEK solutions allow for high network-wide QoS/QoE video performance, reduce overall network management, control costs, enable dynamic service provisioning to meet very fine bandwidth granularities, allow for monitoring of thousands of IPTV streams and dynamic monitoring of video services, and allow for extremely accurate synchronization methods. All of these solutions will help ensure that IPTV based services can meet the viewer's quality expectations under any network conditions.

© 2012 Integrated Photonics Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.



